OOF: Finite Element Analysis of Microstructures
Next: Coordinate Conventions Up: The OOF Manual Previous: /output/cross_section/nonuniform/function Contents
The Element Types
The local constitutive behavior of any part of the OOF model is
incorporated in an element.
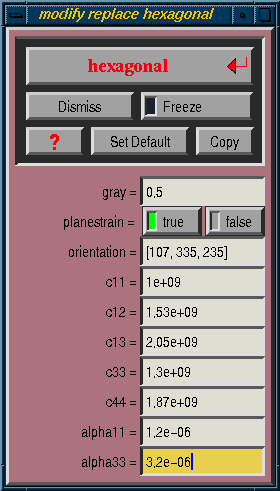
Element properties are specified in a function window, such as /modify/replace/hexagonal, illustrated in Figure 4.1. There is a separate function with its own set of parameters for each type of material. These functions each appear in two menus: /initialize/uniform creates a uniform grid of a given material, and /modify/replace replaces all selected elements with new elements of a given material.
 |
The constitutive parameters derive from linear elasticity and thermoelasticity. Readers familiar with thermoelasticity can skip the background material in section 4.1.
Currently, each element must be treated in either plane strain or plane stress. The distinction between the two is discussed in section 4.2. Plane strain will be used if the variable planestrain in the function window is true.
Element orientations are discussed in Section 4.3.
Subsections
-
- Background Material: Basic Anisotropic Thermoelasticity
- Plane Stress and Plane Strain
- Rotations
- Physical Units
- Element Types and their Parameters
Next: Coordinate Conventions Up: The OOF Manual Previous: /output/cross_section/nonuniform/function Contents /* Send mail to the OOF Team *//* Go to the OOF Home Page */