OOF: Finite Element Analysis of Microstructures
Next: griffith and griffith2 Up: Element Types and their Previous: damisotropic Contents
Subsections
damage
This is an isotropic element with more control over the way
damage is incurred. See Section 4.5.9 for
discussion on mutating elements and damage.
The idea is that the stiffness drop in the direction of maximum tension may be different than the stiffness drop associated with other directions. For instance, if a brick develops a crack it can still support loads in directions which are not normal to the crack plane.
There is one user-defined upper bound and two user-defined knockdown factors.
The process of mutation is the following:
- The maximum principal stress (eigenvalue) is calculated and compared to the specified maximum stress.
- If the maximum specified stress is exceeded, the direction of the principal stress axis is determined. (This direction may be out of the plane.) The stiffness matrix is rotated into a new coordinate system in which the principal stress lies along the z axis.
- In the rotated coordinate system,
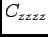 is multiplied by knockdown1. All other components of
is multiplied by knockdown1. All other components of  with at least one of
ijkl=z are multiplied by knockdown2.
with at least one of
ijkl=z are multiplied by knockdown2.
- The stiffness matrix is rotated back into its original orientation.
Parameters
- orientation
- The orientation must be specified, but it has no effect since
the thermoelastic coefficients are isotropic before mutation. The
orientation is calculated in the mutation step, but the element is
rotated and then rotated back, so the orientation after mutation
contains no useful information either.4.5 The
orientation of the principal stress axis is reported in the message
window as elements mutate. [degrees]
- thermoelastic coefficients
- All thermoelastic coefficients for a undamaged damage element are isotropic as
described in section 4.5.1.
- maxstress
- The value to which the maximum principal stress is compared to see if
the element should incur damage when the mutate command is invoked.
See comments in section 4.5.9. [stress]
- knockdown1
- The factor which multiplies the rotated stiffness matrix's
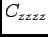 component during a mutation. [dimensionless]
component during a mutation. [dimensionless]
- knockdown2
- The factor which multiplies the rotated stiffness matrix's remaining
 components for at least one of ijkl=z during a
mutation. [dimensionless]
components for at least one of ijkl=z during a
mutation. [dimensionless]
- only_once
- If true, an element which has been damaged during one mutate command will not be damaged further on subsequent mutate
commands. If false, the knockdown factors may be applied multiple
times. Default: false
Next: griffith and griffith2 Up: Element Types and their Previous: damisotropic Contents /* Send mail to the OOF Team *//* Go to the OOF Home Page */