OOF: Finite Element Analysis of Microstructures
Next: trigonalCrack Up: Element Types and their Previous: damage Contents
Subsections
griffith and griffith2
These elements are designed to fail (i.e, mutate (Section
3.1.4)) under the Griffith criterion, which states that a
crack will propagate when the total surface energy required to
propagate the crack can be supplied by the elastic energy stored in
the body:
| (4.1) |
Because elements in OOF can't actually crack, after mutating the elements reduce their moduli anisotropically to simulate a crack, and the amount of surface area generated by mutation has to be estimated. We take it to be the diameter of a circle with the same area as the element.
CAUTION: Neither griffith nor griffith2 is a fully correct implementation of the Griffith criterion. griffith mutates when the stored elastic energy before mutation is greater than the surface energy after mutation, which doesn't account for the fact that there is still some elastic energy left in the element after it mutates. griffith2 solves this problem partially by not including energy due to stress perpendicular to the surface.
The process of mutation is similar to that for the damage element (Section 4.5.10):
- The energy balance for cracking is computed.
- If the energy balance is favorable for cracking, the direction of the maximum principle stress is found.
- Modfication of the stiffness matrix proceeds as in the damage element (Section 4.5.10).
Parameters
- orientation
- As with the damage element, this is meaningless. See the explanation
in Section 4.5.10. [degrees]
- thermoelastic coefficients
- All thermoelastic coefficients for a undamaged damage element are
isotropic as described in section 4.5.1.
- gamma
- The energy per unit length of the crack
surface. [stress/length]4.6
- knockdown1
- The factor which multiplies the rotated stiffness matrix's
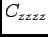 component during a mutation. This should be a small number, if
the element is really to be ``cracked''. [dimensionless]
component during a mutation. This should be a small number, if
the element is really to be ``cracked''. [dimensionless]
- knockdown2
- The factor which multiplies the rotated stiffness matrix's remaining
 components for at least one of ijkl=z during a
mutation. [dimensionless]
components for at least one of ijkl=z during a
mutation. [dimensionless]
- only_once
- If true, an element which has been damaged during one mutate command will not be damaged further on subsequent mutate
commands. If false, the knockdown factors may be applied multiple
times. Default: false
Next: trigonalCrack Up: Element Types and their Previous: damage Contents /* Send mail to the OOF Team *//* Go to the OOF Home Page */