OOF: Finite Element Analysis of Microstructures
Next: valeria Up: Element Types and their Previous: trigonalCrack Contents
Subsections
zimmer and zimmer2
André Zimmermann asked for this element, so we put his name on it.
It's a griffith element, but before it mutates it has hexagonal
symmetry. It has the same problems that the griffith element
does. See Section 4.5.11. Zimmer2 differs from
zimmer in the same way that griffith2 differs from griffith:
the zimmer element mutates if the total stored elastic energy exceeds
the surface energy cost of a crack whereas the zimmer2 element mutates
if the elastic energy due to the maximum principal stress exceeds the
surface energy.
Parameters
- orientation
- The orientation of the hexagonal element before it mutates.
If unrotated (orientation= 0), a hexagonal element is
isotropic in the
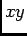 plane (the plane of the screen), with the
crystalline
plane (the plane of the screen), with the
crystalline 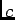 -axis in the
-axis in the 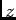 direction (out of the screen).
See Section 4.3.
direction (out of the screen).
See Section 4.3.
- thermoelastic coefficients
- Before mutation, the components of the stiffness matrix are those of
the hexagonal element (Section 4.5.4): c11, c12, c13, c33, and c44. The two independent coefficients
of thermal expansion are alpha11 and alpha33.
- gamma
- The surface energy of the crack.
- knockdown1
- The factor which multiplies the rotated stiffness matrix's
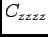 component during a mutation. [dimensionless]
component during a mutation. [dimensionless]
- knockdown2
- The factor which multiplies the rotated stiffness matrix's remaining
 components for at least one of ijkl=z during a
mutation. [dimensionless]
components for at least one of ijkl=z during a
mutation. [dimensionless]
- only_once
- If true, an element which has been damaged during one mutate command will not be damaged further on subsequent mutate
commands. If false, the knockdown factors may be applied multiple
times. Default: false
Next: valeria Up: Element Types and their Previous: trigonalCrack Contents /* Send mail to the OOF Team *//* Go to the OOF Home Page */