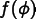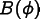OOF2: The Manual
Name
Picard (Picard) — Solve nonlinear equations with Picard iteration. Picard converges more slowly than Newton's method, but does less work per iteration.
Synopsis
Picard(relative_tolerance,absolute_tolerance,maximum_iterations)
Details
-
Base class:
NonlinearSolverBase -
Parameters:
relative_tolerance- Relative tolerance for convergence to a nonlinear solution. Type: A real number.
absolute_tolerance- Absolute tolerance for convergence to a nonlinear solution. Type: A real number.
maximum_iterations- Maximum number of iterations for convergence to a nonlinear solution. Type: Integer.
Description
Picard is a nonlinear
solver used in AdvancedSolverMode for solving nonlinear
equations by Picard iteration.
Given equations of the form
where 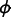 is a vector of unknowns
(
is a vector of unknowns
(Field values), 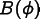 is a nonlinear
matrix-valued function of
is a nonlinear
matrix-valued function of 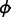 , and
, and 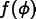 is a vector, and a
trial solution
is a vector, and a
trial solution 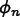 , the next trial
solution is obtained by solving
, the next trial
solution is obtained by solving
Picard iterates this procedure until the
residual, 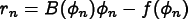 satisfies
satisfies
where  =
=relative_tolerance
and 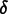 =
=absolute_tolerance,
or when the maximum_iterations limit is exceeded.
![[Note]](IMAGES/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
We've written equation (6.152), which is
being solved by |


![\[ B(\phi)\phi = f(\phi). \]](equations/6.5.2-eq-29.gif)
![\[ B(\phi_n) \phi_{n+1} = f(\phi_n). \]](equations/6.5.2-eq-30.gif)
![\[ |r_n| < \epsilon|r_0| + \delta \]](equations/6.5.2-eq-31.gif)