examples.phase.quaternary¶
Solve a phase-field evolution and diffusion of four species in one-dimension.
The same procedure used to construct the two-component phase field
diffusion problem in examples.phase.binary can be used to build up a
system of multiple components. Once again, we’ll focus on 1D.
>>> from fipy import CellVariable, Grid1D, TransientTerm, DiffusionTerm, ImplicitSourceTerm, PowerLawConvectionTerm, DefaultAsymmetricSolver, Viewer
>>> from fipy.tools import numerix
>>> nx = 400
>>> dx = 0.01
>>> L = nx * dx
>>> mesh = Grid1D(dx = dx, nx = nx)
We consider a free energy density
that is a function of phase
>>> phase = CellVariable(mesh=mesh, name='phase', value=1., hasOld=1)
interstitial components
>>> interstitials = [
... CellVariable(mesh=mesh, name='C0', hasOld=1)
... ]
substitutional components
>>> substitutionals = [
... CellVariable(mesh=mesh, name='C1', hasOld=1),
... CellVariable(mesh=mesh, name='C2', hasOld=1),
... ]
a “solvent” that is constrained by the concentrations of the
other substitutional species, such that
,
>>> solvent = 1
>>> for Cj in substitutionals:
... solvent -= Cj
>>> solvent.name = 'CN'
and temperature
>>> T = 1000
The free energy density of such a system can be written as
where
>>> R = 8.314 # J / (mol K)
is the gas constant. As in the binary case,
is constructed with the free energies of the pure components in each phase, given the “tilting” function
>>> def p(phi):
... return phi**3 * (6 * phi**2 - 15 * phi + 10)
and the “double well” function
>>> def g(phi):
... return (phi * (1 - phi))**2
We consider a very simplified model that has partial molar volumes
for the “interstitials” and
for the “substitutionals”.
This approximation has been used in a number of models where density
effects are ignored, including the treatment of electrons in
electrodeposition processes [25] [26]. Under these
constraints
and
where and where
is the classical chemical potential of
component
for the binary species and
is the total molar density.
>>> rho = 1.
>>> for Cj in interstitials:
... rho += Cj
and
are the partial derivatives of of
and
with respect to
>>> def pPrime(phi):
... return 30. * g(phi)
>>> def gPrime(phi):
... return 2. * phi * (1 - phi) * (1 - 2 * phi)
We “cook” the standard potentials to give the desired solid and liquid concentrations, with a solid phase rich in interstitials and the solvent and a liquid phase rich in the two substitutional species.
>>> interstitials[0].S = 0.3
>>> interstitials[0].L = 0.4
>>> substitutionals[0].S = 0.4
>>> substitutionals[0].L = 0.3
>>> substitutionals[1].S = 0.2
>>> substitutionals[1].L = 0.1
>>> solvent.S = 1.
>>> solvent.L = 1.
>>> for Cj in substitutionals:
... solvent.S -= Cj.S
... solvent.L -= Cj.L
>>> rhoS = rhoL = 1.
>>> for Cj in interstitials:
... rhoS += Cj.S
... rhoL += Cj.L
>>> for Cj in interstitials + substitutionals + [solvent]:
... Cj.standardPotential = R * T * (numerix.log(Cj.L/rhoL)
... - numerix.log(Cj.S/rhoS))
>>> for Cj in interstitials:
... Cj.diffusivity = 1.
... Cj.barrier = 0.
>>> for Cj in substitutionals:
... Cj.diffusivity = 1.
... Cj.barrier = R * T
>>> solvent.barrier = R * T
We create the phase equation
with a semi-implicit source just as in examples.phase.simple and
examples.phase.binary
>>> enthalpy = 0.
>>> barrier = 0.
>>> for Cj in interstitials + substitutionals + [solvent]:
... enthalpy += Cj * Cj.standardPotential
... barrier += Cj * Cj.barrier
>>> mPhi = -((1 - 2 * phase) * barrier + 30 * phase * (1 - phase) * enthalpy)
>>> dmPhidPhi = 2 * barrier - 30 * (1 - 2 * phase) * enthalpy
>>> S1 = dmPhidPhi * phase * (1 - phase) + mPhi * (1 - 2 * phase)
>>> S0 = mPhi * phase * (1 - phase) - S1 * phase
>>> phase.mobility = 1.
>>> phase.gradientEnergy = 25
>>> phase.equation = TransientTerm(coeff=1/phase.mobility) \
... == DiffusionTerm(coeff=phase.gradientEnergy) \
... + S0 + ImplicitSourceTerm(coeff = S1)
We could construct the diffusion equations one-by-one, in the manner of
examples.phase.binary, but it is better to take advantage of the full
scripting power of the Python language, where we can easily loop over
components or even make “factory” functions if we desire. For the
interstitial diffusion equations, we arrange in canonical form as before:
>>> for Cj in interstitials:
... phaseTransformation = (rho.harmonicFaceValue / (R * T)) \
... * (Cj.standardPotential * p(phase).faceGrad
... + 0.5 * Cj.barrier * g(phase).faceGrad)
...
... CkSum = CellVariable(mesh=mesh, value=0.)
... for Ck in [Ck for Ck in interstitials if Ck is not Cj]:
... CkSum += Ck
...
... counterDiffusion = CkSum.faceGrad
...
... convectionCoeff = counterDiffusion + phaseTransformation
... convectionCoeff *= (Cj.diffusivity
... / (1. + CkSum.harmonicFaceValue))
...
... Cj.equation = (TransientTerm()
... == DiffusionTerm(coeff=Cj.diffusivity)
... + PowerLawConvectionTerm(coeff=convectionCoeff))
The canonical form of the substitutional diffusion equations is
>>> for Cj in substitutionals:
... phaseTransformation = (solvent.harmonicFaceValue / (R * T)) \
... * ((Cj.standardPotential - solvent.standardPotential) * p(phase).faceGrad
... + 0.5 * (Cj.barrier - solvent.barrier) * g(phase).faceGrad)
...
... CkSum = CellVariable(mesh=mesh, value=0.)
... for Ck in [Ck for Ck in substitutionals if Ck is not Cj]:
... CkSum += Ck
...
... counterDiffusion = CkSum.faceGrad
...
... convectionCoeff = counterDiffusion + phaseTransformation
... convectionCoeff *= (Cj.diffusivity
... / (1. - CkSum.harmonicFaceValue))
...
... Cj.equation = (TransientTerm()
... == DiffusionTerm(coeff=Cj.diffusivity)
... + PowerLawConvectionTerm(coeff=convectionCoeff))
We start with a sharp phase boundary
>>> x = mesh.cellCenters[0]
>>> phase.setValue(1.)
>>> phase.setValue(0., where=x > L / 2)
and with uniform concentration fields, initially equal to the average of the solidus and liquidus concentrations
>>> for Cj in interstitials + substitutionals:
... Cj.setValue((Cj.S + Cj.L) / 2.)
If we’re running interactively, we create a viewer
>>> if __name__ == '__main__':
... viewer = Viewer(vars=([phase]
... + interstitials + substitutionals
... + [solvent]),
... datamin=0, datamax=1)
... viewer.plot()
and again iterate to equilibrium
>>> solver = DefaultAsymmetricSolver(tolerance=1e-10)
>>> dt = 10000
>>> from builtins import range
>>> for i in range(5):
... for field in [phase] + substitutionals + interstitials:
... field.updateOld()
... phase.equation.solve(var = phase, dt = dt)
... for field in substitutionals + interstitials:
... field.equation.solve(var = field,
... dt = dt,
... solver = solver)
... if __name__ == '__main__':
... viewer.plot()
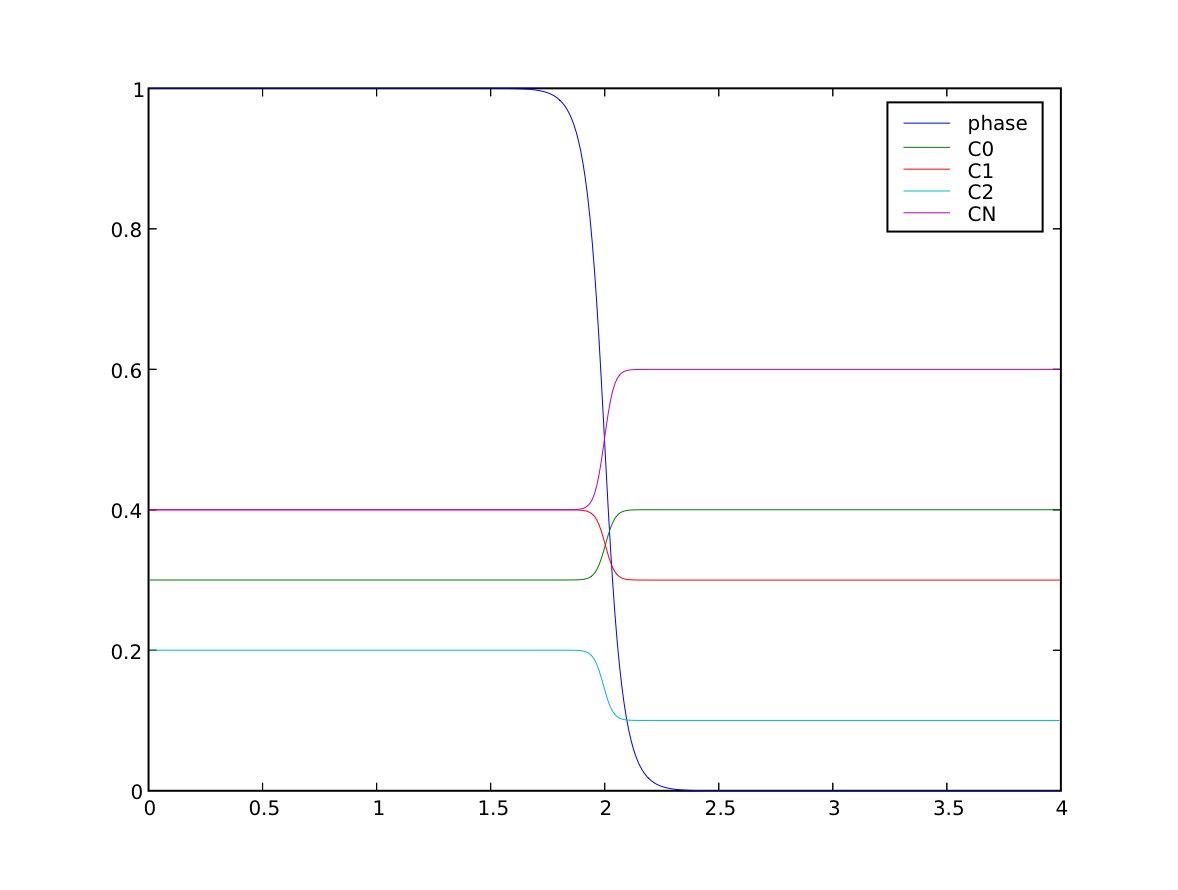
We can confirm that the far-field phases have remained separated
>>> X = mesh.faceCenters[0]
>>> print(numerix.allclose(phase.faceValue[X.value==0], 1.0, rtol = 1e-5, atol = 1e-5))
True
>>> print(numerix.allclose(phase.faceValue[X.value==L], 0.0, rtol = 1e-5, atol = 1e-5))
True
and that the concentration fields have appropriately segregated into their equilibrium values in each phase
>>> equilibrium = True
>>> for Cj in interstitials + substitutionals:
... equilibrium &= numerix.allclose(Cj.faceValue[X.value==0], Cj.S, rtol = 3e-3, atol = 3e-3).value
... equilibrium &= numerix.allclose(Cj.faceValue[X.value==L], Cj.L, rtol = 3e-3, atol = 3e-3).value
>>> print(equilibrium)
True
 FiPy
FiPy