examples.diffusion.mesh20x20¶
Solve a two-dimensional diffusion problem in a square domain.
This example solves a diffusion problem and demonstrates the use of applying boundary condition patches.
>>> from fipy import CellVariable, Grid2D, Viewer, TransientTerm, DiffusionTerm
>>> from fipy.tools import numerix
>>> nx = 20
>>> ny = nx
>>> dx = 1.
>>> dy = dx
>>> L = dx * nx
>>> mesh = Grid2D(dx=dx, dy=dy, nx=nx, ny=ny)
We create a CellVariable and initialize it to zero:
>>> phi = CellVariable(name = "solution variable",
... mesh = mesh,
... value = 0.)
and then create a diffusion equation. This is solved by default with an iterative conjugate gradient solver.
>>> D = 1.
>>> eq = TransientTerm() == DiffusionTerm(coeff=D)
We apply Dirichlet boundary conditions
>>> valueTopLeft = 0
>>> valueBottomRight = 1
to the top-left and bottom-right corners. Neumann boundary conditions are automatically applied to the top-right and bottom-left corners.
>>> X, Y = mesh.faceCenters
>>> facesTopLeft = ((mesh.facesLeft & (Y > L / 2))
... | (mesh.facesTop & (X < L / 2)))
>>> facesBottomRight = ((mesh.facesRight & (Y < L / 2))
... | (mesh.facesBottom & (X > L / 2)))
>>> phi.constrain(valueTopLeft, facesTopLeft)
>>> phi.constrain(valueBottomRight, facesBottomRight)
We create a viewer to see the results
>>> if __name__ == '__main__':
... viewer = Viewer(vars=phi, datamin=0., datamax=1.)
... viewer.plot()
and solve the equation by repeatedly looping in time:
>>> timeStepDuration = 10 * 0.9 * dx**2 / (2 * D)
>>> steps = 10
>>> from builtins import range
>>> for step in range(steps):
... eq.solve(var=phi,
... dt=timeStepDuration)
... if __name__ == '__main__':
... viewer.plot()
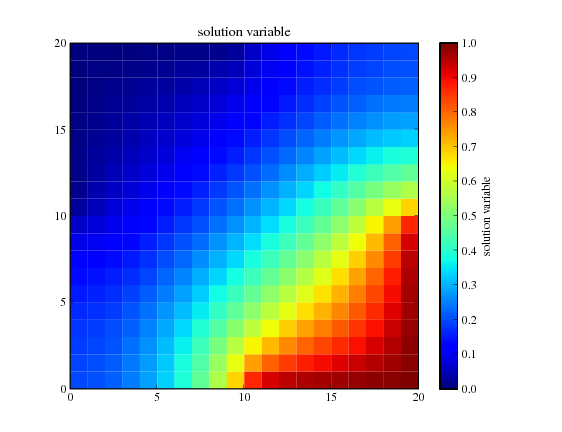
We can test the value of the bottom-right corner cell.
>>> print(numerix.allclose(phi(((L,), (0,))), valueBottomRight, atol = 1e-2))
1
>>> from fipy import input
>>> if __name__ == '__main__':
... input("Implicit transient diffusion. Press <return> to proceed...")
We can also solve the steady-state problem directly
>>> DiffusionTerm().solve(var=phi)
>>> if __name__ == '__main__':
... viewer.plot()
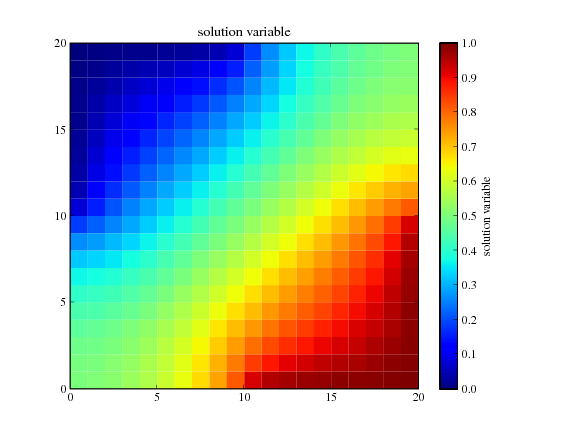
and test the value of the bottom-right corner cell.
>>> print(numerix.allclose(phi(((L,), (0,))), valueBottomRight, atol = 1e-2))
1
>>> from fipy import input
>>> if __name__ == '__main__':
... input("Implicit steady-state diffusion. Press <return> to proceed...")
Last updated on Jun 27, 2023.
Created using Sphinx 6.2.1.
 FiPy
FiPy