examples.diffusion.nthOrder.input4thOrder1D¶
Solve a fourth-order diffusion problem.
This example uses the DiffusionTerm class to solve the equation
on a 1D mesh of length
>>> L = 1000.
We create an appropriate mesh
>>> from fipy import CellVariable, Grid1D, NthOrderBoundaryCondition, DiffusionTerm, Viewer, GeneralSolver
>>> nx = 500
>>> dx = L / nx
>>> mesh = Grid1D(dx=dx, nx=nx)
and initialize the solution variable to 0
>>> var = CellVariable(mesh=mesh, name='solution variable')
For this problem, we impose the boundary conditions:
or
>>> alpha1 = 2.
>>> alpha2 = 1.
>>> alpha3 = 4.
>>> alpha4 = -3.
>>> BCs = (NthOrderBoundaryCondition(faces=mesh.facesLeft, value=alpha3, order=2),
... NthOrderBoundaryCondition(faces=mesh.facesRight, value=alpha4, order=3))
>>> var.faceGrad.constrain([alpha2], mesh.facesRight)
>>> var.constrain(alpha1, mesh.facesLeft)
We initialize the steady-state equation
>>> eq = DiffusionTerm(coeff=(1, 1)) == 0
>>> import fipy.solvers.solver
>>> if fipy.solvers.solver == 'petsc':
... solver = GeneralSolver(precon='lu')
... else:
... solver = GeneralSolver()
We perform one implicit timestep to achieve steady state
>>> eq.solve(var=var,
... boundaryConditions=BCs,
... solver=solver)
The analytical solution is:
or
>>> analytical = CellVariable(mesh=mesh, name='analytical value')
>>> x = mesh.cellCenters[0]
>>> analytical.setValue(alpha4 / 6. * x**3 + alpha3 / 2. * x**2 + \
... (alpha2 - alpha4 / 2. * L**2 - alpha3 * L) * x + alpha1)
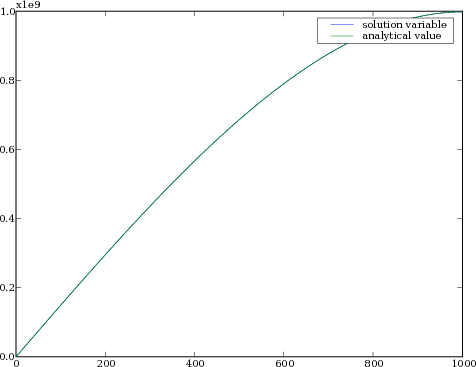
>>> print(var.allclose(analytical, rtol=1e-4))
1
If the problem is run interactively, we can view the result:
>>> if __name__ == '__main__':
... viewer = Viewer(vars=(var, analytical))
... viewer.plot()
Last updated on Jun 27, 2023.
Created using Sphinx 6.2.1.
 FiPy
FiPy