|
|

Measure: A Polytope Analysis Tool
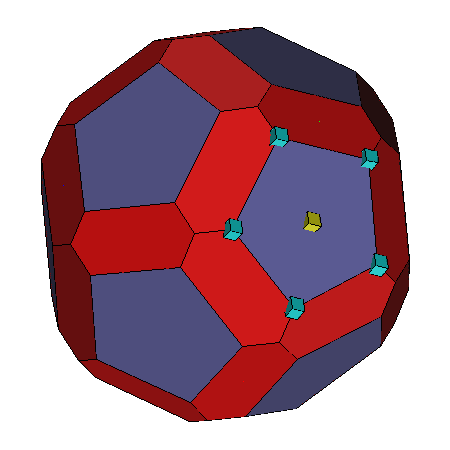
Table of Contents
Measure is a program for interactively examining the
geometrical properties of polyhedra that are being viewed with
Geomview. Using Measure, a user can determine the area of
facets, the length of edges, the coordinates of a vertex (or point),
and the distance between points.
Instructions
Measure determines the geometrical properties of objects
within Geomview, and as such, a coordinate system must be defined.
The default is to measure properties in "Object" coordinates; to
measure properties in "World" coordinates, push the Global
button.
- Facet properties :
Select a facet of interest;
its bounding vertices are indicated, and the area and normal are
displayed by Measure.
- Edge Properties :
Select an edge, and measure
displays its length and direction.
- Vertex Properties :
Select a vertex, and measure
displays its (xyz) coordinates.
- Distance between Points :
Select a reference
point by clicking the Set button; this makes the currently
active point magenta. Hereafter, the distance from the reference
point to the current "picked" point will be displayed, as will the
angle between the vector of the referenced object and the vector of
the currently picked object. A new reference point can be selected by
clicking on Set again.
The basic
operation of the program involves simply selecting an object (vertex,
edge, facet) by right-clicking with the mouse. The object selected is
indicated in Geomview by placing indicator boxes on the polytope;
information about this object is then displayed in the Measure
window.
NOTE: Selection of objects in some versions of
Geomview is more precise than in others. Occasionally, selection of
one vertex, for example, will yield another.
| 
| 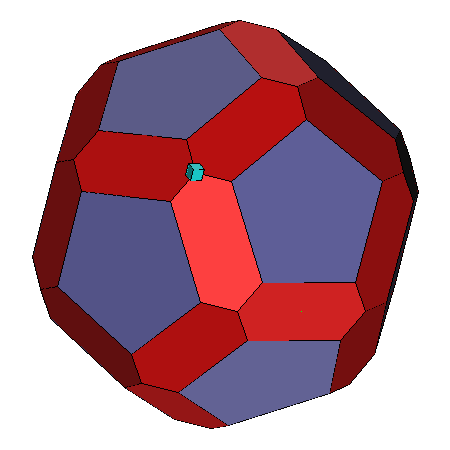 |
| Facet: Selection of a facet results in a
yellow box being placed at the Picked Point and cyan boxes
being placed on the vertices of
that facet. |
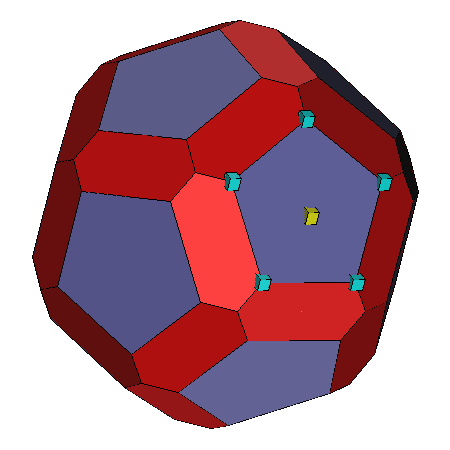
Edge:
Selection of an edge results in a yellow box at the
picked point and cyan boxed at the vertices that bound the edge. |
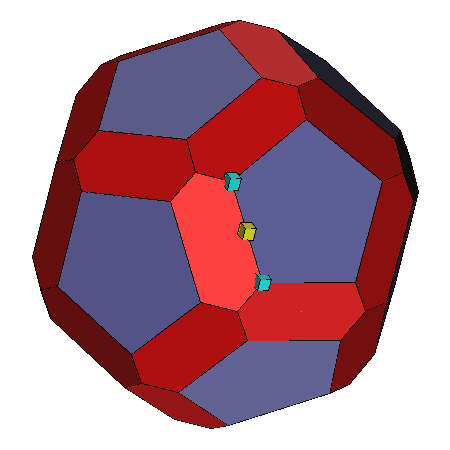
Vertex: Selection of a vertex yields only a
cyan box at that vertex |
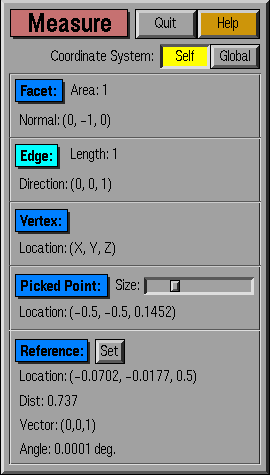
The information displayed in the Measure window is a function of
the objects that have been selected. Selection of a facet, edge, or
vertex causes the corresponding box to become bright blue. The
following information is displayed in Measure:
- Facet: The area and normal of the selected facet
- Edge: The length and direction of the selected facet
- Vertex: The coordinates (xyz) of the selected
vertex
Some information is displayed regardless of what object has been
selected. The Picked Point is the point that was selected by
right-clicking the mouse. Reference is a feature that allows distance
and angle between two points to be computed. One point is set as the
reference point, and thereafter, the distance is displayed from the
Reference point to the Picked Point.
- Picked Point: The coordinates (xyz) of the selected
point. The slider enables resizing of all points (smallest to largest
point size, left to right).
- Reference: Clicking the Set button makes
the currently selected point the reference (indicated by a magenta
box). After selecting a reference, the distance to the picked point
will be displayed to the right of Set, and the angle between the last
picked feature's vector and the current one will be shown. For faces,
the defining vector is a normal, for edges a tangent, and for corners,
the vector from the origin.
Measure is a module for use with Geomview . As
such, it is useless unless Geomview is installed. Measure is provided
in binary distribution. If unavailable for
your specific platform, download the Measure source code and compile.
UNIX commands begin with a '%' or are in italics.
- Binary distribution
- Download
- Extract archive:
% uncompress measure32_sgi.Z
- Install Measure as a
Geomview module
- Installation from Source
Download the Xforms library in binary format for the platform of
interest from the Xforms web
site. Uncompress and extract the Xforms archive and
follow the instructions in README.txt for
installation.
Measure requires an OOGL library for compilation that can
be obtained by compiling Geomview from source. It
doesn't matter whether Geomview compiles cleanly, as long
as liboogl.a is created. In addition, Measure
requires some Geomview header files that are not
available without installing from source. Hence,
installation of measure depends on whether the version of
Geomview at your site was compiled from source (Case I)
or obtained from the binary distribution (Case II).
Case I (Geomview compiled from source)
- Locate Geomview Installation directory (gv_dir)
- Locate relevant Geomview header (*.h) files:
(Default = gv_dir/Geomview/include)
- Locate liboogl.a:
(Default gv_dir/lib)
- Make directory for measure source:
% mkdir meas_dirname
% cd meas_dirnam
- Download
Measure source (14K)
- Extract the source archive:
% zcat measure_1.1_src.tar.Z | tar xvf -
- Modify Makefile variables GVINCLDIR and GVLIBDIR.
Note: On Linux systems, you must do
the final link using g++, since the geomview archive
requires some c++ symbols.
- Compile Codes:
% make measure
- Install Measure as a
Module to Geomview
Case II (Geomview installed from binary
distribution)
- Create Geomview root directory:
% mkdir gv_root
- Download Geomview
source into gv_root
- Extract Geomview distribution into gv_root:
% zcat geomview-1.8.1.tar.gz | tar xvf -
- Compile Geomview:
% cd Geomview
% make
- Download
Measure source
- Extract the source archive:
% zcat measure_1.1_src.tar.Z | tar xvf -
- Modify Makefile to reflect at least:
GVINCLDIR = -I/full_path_name/gv_root/Geomview/include
GVLIBDIR = -L/full_path_name/gv_root/Geomview/lib/mach_name
Note: On Linux systems, you must do
the final link using g++, since the geomview archive
requires some c++ symbols.
- Compile Codes:
% make measure
- Install Measure as a
Module to Geomview
Credits
Measure was written by:
Andrew Roosen
Ceramics Division / Center for Theoretical and Computational Materials
Science
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Documentation by:
Ryan McCormack
Ceramics Division / Center for Theoretical and Computational Materials
Science
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Center for Theoretical and Computational Materials Science, NIST
Questions or comments:
[email protected]
|
|









