- ...distributivity.
- The
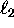 inner product is commonly written as the ``dot'' product:
inner product is commonly written as the ``dot'' product:
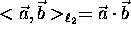 .
We use the `dot'-notation exclusively for
.
We use the `dot'-notation exclusively for 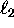 for inner products on vectors
and (described below) use the `dot'-notation for the
for inner products on vectors
and (described below) use the `dot'-notation for the 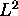 inner product on
functions.
inner product on
functions.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...density
- This
relation between
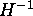 and
and 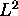 is implicit in the variational
method employed in [3].
is implicit in the variational
method employed in [3].
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...zero
-
The integral over the boundary
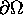 usually vanishes identically, either because admissible
flows v vanish on
usually vanishes identically, either because admissible
flows v vanish on 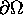 (Dirichlet conditions), or
because the function which is projected onto the boundary (which depends on derivatives of f with
respect to its gradient and higher order-derivatives) in the boundary integral vanishes (Neumann
conditions).
If neither condition holds, then the boundary term must also be included in the
variation.
(Dirichlet conditions), or
because the function which is projected onto the boundary (which depends on derivatives of f with
respect to its gradient and higher order-derivatives) in the boundary integral vanishes (Neumann
conditions).
If neither condition holds, then the boundary term must also be included in the
variation.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...equation
-
These equations, including the Allen-Cahn equation below,
is sometimes written with
 -terms multiplying both the gradient term
and the homogeneous part:
-terms multiplying both the gradient term
and the homogeneous part:
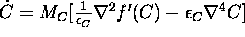 .
This form has some advantages for the investigation of asymptotic behavior of of small
.
This form has some advantages for the investigation of asymptotic behavior of of small  .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.