OOF2: The Manual
Name
Mechanical:Elasticity:Isotropic — Isotropic linear elasticity.
Details
- Property Category: Elasticity
-
Parameters:
cijkl- Type: An object of the
IsotropicRank4Tensorclass.
-
Fields:
Displacement -
Fluxes:
Stress
Discussion
The isotropic elasticity Property specifies that the Stress depends linearly and isotropically on the
gradients of the Displacement,
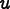 :
:
where 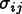 is the Stress,
is the Stress, 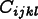 is an isotropic
fourth rank tensor given by the modulus
is an isotropic
fourth rank tensor given by the modulus cijkl,
and  is the linear
geometric strain,
is the linear
geometric strain,
This form of the strain is not invariant under rigid rotations and is inappropriate for problems with large strains, which should use large strain elastic properties instead.


![\[ \sigma_{ij} = C_{ijkl}\epsilon_{kl} \]](equations/6.4.1-eq-1.gif)
![\[ \epsilon_{ij} = \frac12\left(\frac{\partial u_i}{\partial x_j}
+ \frac{\partial u_j}{\partial x_i}\right). \]](equations/6.4.1-eq-2.gif)

